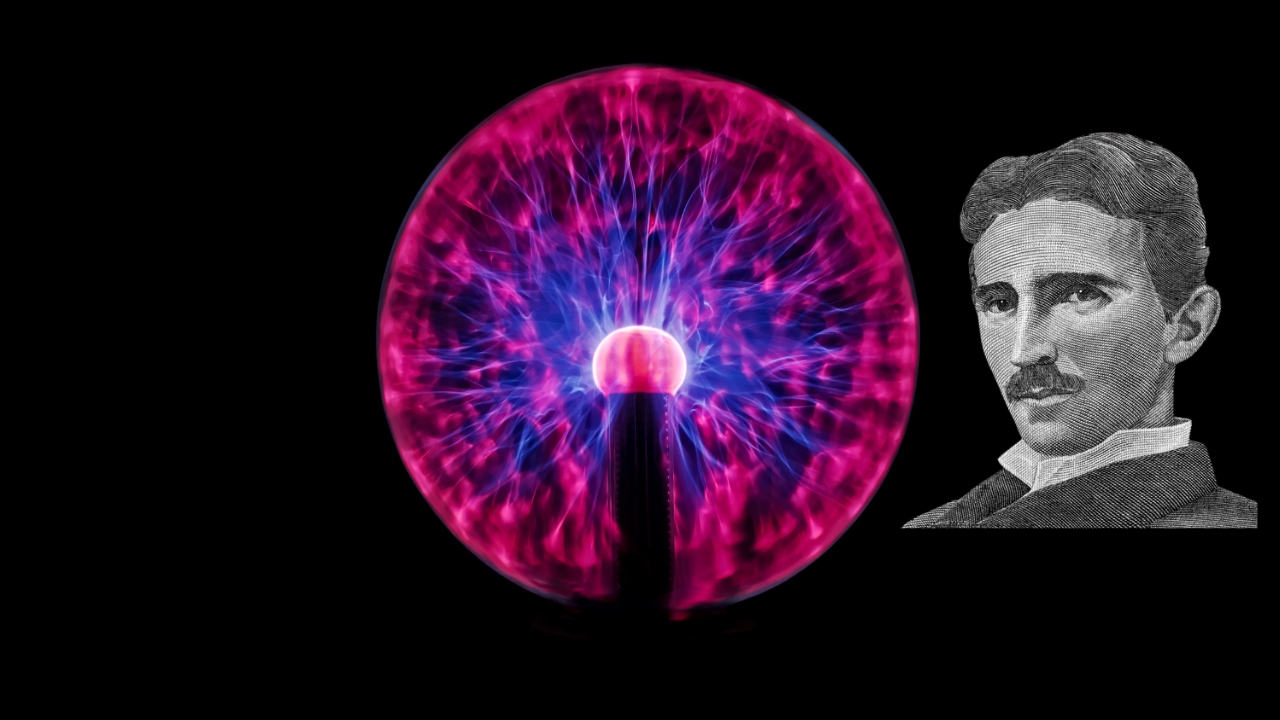
One of the most remarkable inventors in history is Nikola Tesla, whose name is linked with creativity and intellect. In addition to influencing our destiny, his outstanding contributions to science and technology have radically altered the path of human civilization. Tesla, who was born on July 10, 1856, in Smiljan, Croatia, has forever changed the course of human history. We’ll explore some of his ground-breaking inventions and their significant influence on our society in this blog.
Revolutionizing Electricity with AC Power
One of Tesla’s most significant and revolutionary achievements was the creation of the alternating current (AC) electrical system. Thomas Edison’s direct current (DC) method dominated the late 19th century, but Tesla’s AC system revolutionized the industry. It had many benefits, the main one being that electricity could be sent across great distances with little power loss. At Niagara Falls, the first hydroelectric power plant was built because to Tesla’s work on AC electricity. The start of widespread electrification was signaled by this plant, which supplied energy to Buffalo, New York.
Tesla’s AC power system revolutionized entire industries and made electricity more widely and affordably available, not just for our homes. It made it possible for the development of electric machinery, lights, and appliances, drastically transforming how people lived and worked. Furthermore, the use of AC electricity set the stage for the development of the contemporary electrical grid, which makes it possible to electrify whole countries today.
The Tesla Coil
One of his tools for electrical experimentation was the Tesla coil, which bears his name. It established the groundwork for wireless technology even though it didn’t have many useful applications at the time. It also became a symbol of innovation. Working with high-frequency electricity was made possible for him by this coil, and it would eventually play a significant role in wireless and radio communication.
Wireless communication and Wi-Fi technologies are a direct result of Tesla’s wireless power transmission research. Long before these concepts found practical application in our daily lives, he was investigating them.
Wireless Communication
Tesla created the “Tesla oscillator,” an apparatus that produces electromagnetic waves, as a result of his research with high-frequency radio waves. Tesla made significant contributions to the radio’s invention, even though Guglielmo Marconi is frequently given credit for it. He asserted that he had accomplished long-distance signal transmission prior to Marconi’s well-known work and filed numerous radio-related patents. Eventually, Tesla’s radio technology patent was reinstated in honor of his groundbreaking work.
Claiming the Radio Waves
Guglielmo Marconi, who is largely credited with creating the radio, frequently eclipses Tesla’s contributions to wireless communication. Still, it’s critical to acknowledge Tesla’s enormous achievements in this field.
Tesla submitted a number of radio-related patent applications, and much before Marconi’s well-known work, he had successfully transmitted radio signals across long distances. Indeed, in 1943, the U.S. Supreme Court decided that earlier claims by Tesla and other inventors rendered several of Marconi’s most important patents null and void. This ruling in court recognized Tesla’s.
The Lost Wardenclyffe Tower
Building the Wardenclyffe Tower on Long Island, New York, was one of Tesla’s most ambitious undertakings. The tower was supposed to serve as a wireless transmission facility for international communication. Tesla wanted to develop a system that could transmit data and energy wirelessly over the world.
Though it was never finished due to financial difficulties, Tesla’s big vision of a wirelessly connected world was embodied in the Wardenclyffe Tower project. Even though he did not live to see his goal come true, it demonstrated his faith in the potential of wireless technology.
Wireless Communication Today
In many ways, Tesla’s idea of wireless communication has come to pass in the contemporary period. One immediate offshoot of Tesla’s work on wireless transmission is Wi-Fi technology. We now rely heavily on Wi-Fi networks to facilitate wireless internet connections, which let us access information, communicate, and work from almost anywhere.
The concepts of wireless transmission have also transformed mobile communication, in addition to Wi-Fi. Wireless networks enable our smartphones—which have evolved into virtual extensions of ourselves—to link us to the internet, other gadgets, and people globally.
Remote Control
Another example of Tesla’s innovative thinking is his work on remote control devices. He built a remote-controlled boat, which at the time was a revolutionary invention. It foretold the creation of remote controllers for a variety of modern applications, including televisions, drones, and numerous more, which have now become commonplace in society.
X-Ray Technology
Tesla’s investigation into high-frequency electrical currents produced important advancements in the field of X-ray technology. Tesla’s vacuum tube experiments advanced our understanding of X-rays, despite the fact that Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen is widely acknowledged as the person who discovered them. Since then, non-invasive diagnostic methods have been made possible by X-ray technology, which has also saved numerous lives in the medical field.
Induction Motors
The induction motor, developed by Tesla, had a profound effect on industry and engineering. These dependable and efficient motors are widely utilized in many different industries, including domestic appliances, transportation, and manufacturing. Their implementation has had a significant impact on industrial operations and energy usage.

 AI2 years ago
AI2 years ago
 Blog2 years ago
Blog2 years ago
 NASA2 years ago
NASA2 years ago
 AI2 years ago
AI2 years ago
 Space2 years ago
Space2 years ago
 Blog2 years ago
Blog2 years ago
 NASA2 years ago
NASA2 years ago
 NASA2 years ago
NASA2 years ago